All entries for Saturday 01 August 2015
August 01, 2015
Ain't talkin' 'bout love. Roman "Spintriae" in context.
 |
| Roman token, found in the Thames, PAS LON-E98F21 |
In 2012 this token was found in the Thames in London, resulting in numerous news articles about this 'brothel token'. The obverse carries the Roman numeral XIIII (14), while the reverse carries a sex scene. The couple are laying on a decorated bed or a couch, the woman laying on her front while a male straddles her.
This token is part of a broader series that carry a Roman numeral between 1 and 16 on one side, and various sex acts on the other. Another series carry Roman numerals on one side and portraits of Augustus, Tiberius or Livia on the other (see below). Buttrey analysed the dies of both series and concluded they were connected; he suggested that these objects date to the Julio-Claudian period and were perhaps gaming tokens, envisaging a possible scenario where one side played 'the imperial portraits' and the other 'the sex scenes', making the game a form of salacious gossip on the sex lives of the Roman emperors.
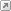
 |
| Roman token showing Tiberius and XII within wreath. |
In reality, we know very little about these objects; their sexual scenery has created numerous forgeries, and very few archaeological contexts are known. They are often called spintriae, a label created in the modern era from a reading of Suetonius' Life of Tiberius. As part of the portrayal of Tiberius' activities on Capri, Suetonius records the presence of numerous female and male prostitutes, called spintrias (Suet. Tib. XLIII, see also Tacitus, Ann. VI.1; sphinthria or spintria referred to a male prostitute in Latin, from the Greek σφιγκτήρ, and connected to the Latin/modern word sphincter). It is this tale that inspired early collectors and scholars to label these objects spintriae, and when a hoard of tokens was found on Capri it cemented the name, though they were not called this in antiquity.
Indeed, the known find contexts of these objects suggest they had little to do with sex. Although hundreds of these specimens exist (precise numbers are difficult given the quantity of fakes in existence), only a handful of closed archaeological contexts are known. We cannot know whether the Thames example was lost in antiquity, or more recently. But one example was recently found in a tomb in Mutina; associated ceramics and other coins dates the tomb to AD 22-57, suggesting Buttrey's dating of the Julio-Claudian period is correct. Another was found during an archaeological campaign on the island of Majsan; this was pierced, suggesting it had been transformed into a piece of jewellery. Scattered other examples are reported to have been found in Caesarea Maritima, in the Garigliano in Italy, on Skegness beach (likely a modern loss) and in Germany (Stockstadt am Main, Saalburg, Nendorp-Wischenborg; these are sporadic finds). Although the information on the find places of these objects leaves much to be desired, none of these find spots are brothels, and in each example there is only one 'spintria' found. What their purpose was remains a mystery. Like many Roman tokens, much more study is required before we can fully understand these objects.

This month's coin was chosen by Clare Rowan. Clare is a research fellow at Warwick, who has recently become interested in the role tokens had in Roman society.
Coin images above reproduced courtesy of the Portable Antiquities Scheme and © The Trustees of the British Museum
Select Bibliography:
Benassi, F., N. Giordani and C. Poggi (2003). Una tessera numerale con scena erotica da un contesto funerario di Mutina. Numismatica e Antichità classiche 32: 249-273.
Buttrey, T. (1973). The spintriae as a historical source. Numismatic Chronicle 13: 52-63.
Martini, R. (1997). Tessere numerali bronzee romane nelle civiche raccolte numismatiche del comune di Milano Parte I. Annotazione Numismatische Supplemento IX: 1-28.
Mirnik, I. (1985). Nalazi novca s Majsana. VAMZ 18: 87-96.
 Clare Rowan
Clare Rowan

 Please wait - comments are loading
Please wait - comments are loading
 Loading…
Loading…