All 5 entries tagged Cairngorm
View all 7 entries tagged Cairngorm on Warwick Blogs | View entries tagged Cairngorm at Technorati | There are no images tagged Cairngorm on this blog
December 28, 2008
WiMIC Browser v.3 – MySQL, BlazeDS, Lucene, Spring, Flex 3.0, Cairngorm
Follow-up to WiMIC Browser v.2 – migrated to Adobe Flex Cairngorm application framework from Transversality - Robert O'Toole
I've taken advantage of some new technologies to redevelop the Women in Modern Irish Culture data browser. The application will eventually give full online access to a big biographical and bibliographical database developed by researchers at Warwick and University College Dublin. The last version was rather over-complicated and ponderous, giving slow and awkward access to the data. This new version provides a much more instantaneous view onto the thousands of records. It is now really a data browser rather than just a search tool. Researchers can immediately scan through thousands of records, which are all immediately loaded into data grids. Whereas the old version served up 12 records at a time as a result of database queries via JSON, the new version can serve up over 9000 records in a few seconds, using the highly efficient BlazeDS mechanism.
Rapid data browsing with BlazeDS
This is how it works:
- the Flex/Flash interface calls a method on a Remote Object that will return an ArrayCollection of Author objects;
- the RemoteObject proxies through to a corresponding method in a class exposed via BlazeDS;
- the Java method is in fact a Spring bean which queries the database using Spring's jdbc utils (the data is now on MySQL rather than SQL Server);
- Spring builds a Flash Remoting ArrayCollection of Author objects (corresponding to my Flex Author class);
- the ArrayCollection is returned as the result of the proxied method using the effiiciently compressed AMF protocol;
- the ArrayCollection is added to the Flex Cairngorm model, to which the datagrid is bound;
- the data appears in the grid, and can be browsed and re-ordered instantly.
Even when retrieving all 9000+ authors, that only takes a few seconds.
The authors are listed in an AdvancedDataGrid, allowing the researcher to drill down into a selected record. This retrieves further data about the selected author (using BlazeDS) including a list of publications.
Fast and smart querying with Lucene
In addition, I have used the Lucene Java library to add query interfaces that search pre-built indexes. Lucene performs free-text and exact searching as required, and also uses synonyms. So, for example, a researcher could search for "Dublin AND poetry" in the simple search form, and see almost instantly all authors with the words "Dublin" AND "poetry" in their records (including their publications). It would also list records containing "poem" and "poems", giving them a lower ranking in the results.
To be even more precise, one can search for "Locations:Dublin AND Genres:poetry" which would return only authors of poetry with some association with Dublin. "Locations" and "Genres" being fields in the Lucene index. I'm using that mechanism to create a search interface with specific fields such as "genre", "surname", "firstname", "publication title" and "location".
As with other queries, BlazeDS is used for highly efficient transmission of results.
A further addition, again using BlazeDS and Lucene, is the ability to list authors who had published in a selected decade. Each author record in the Lucene index contains a list of the decades in which they published. The efficiency of this approach is demonstrated by viewing all authors to have published since 2000.
Now that I have all of these elements in place, I'll be able to quickly add more features and richer data, including more information on publications.
September 06, 2007
WiMIC Browser v.2 – migrated to Adobe Flex Cairngorm application framework
Follow-up to WiMIC Browser – my first big Flex application from Transversality - Robert O'Toole
The application behaves just as before, but the plumbing behind it has been rationalised and improved using Cairngorm. The project now looks like this in the Navigator:

The migration was quite straightforwards. The design of the original app was quite similar to that of a Cairngorm app. However, the framework offers a few neat tricks:
- A simple and easy to understand event based controller. Views can initiate events, which are then passed onto the required command by the controller. Once the event is called, the originating view is forgotten about.
- The AppModelLocator singleton, which gives access to centrally stored value objects. Elements in views are bound directly to value objects and properties in the model. If a command updates the model, then changes are made to the bound elements.
- In this app, tab navigators are used to contain the various views. The TabNavigator.selectedIndex property of each tab navigator is bound to a property in the model. That means that a command can change the currently displayed tab by changing the relevant property in the model.
- Chaining of commands – a command can call another command. For example, when viewing a single publication record, the GetSinglePublication command calls further commands depending upon the type of publication that is being viewed.
August 29, 2007
Adobe Flex in an afternoon – possible course
Follow-up to Cairngorm Flex Quickstart from Transversality - Robert O'Toole
It’s possible. If we do it, then this would be the course material. I reckon (optimistically) that it could be covered in half a day….
1. What is Flex capable of?
1.1 What is a Rich Internet Application
1.2 Examples
1.2.1 Databases (and Hibernate)
1.2.2 XML and RSS
1.2.3 Charting
1.2.4 Video and audio
1.2.5 The Adobe Internet Runtime
2. The development process
2.1 Introduction to Eclipse and FlexBuilder
2.2 Debugging and inspecting
2.3 The Cairngorm framework
3. Designing an application as a set of user interface views
3.1 Creating a view as a custom component
3.2 Indexing views in a ViewStack (and other navigation controls)
3.3 Using Flex components to build user interface views
3.3.1 Using containers to control layout (canvas, vbox, hbox, panel)
3.3.2 Using Flex interface controls (label, text, textarea, button, datagrid, list, tree)
3.3.3 Binding controls to data
4. Encapsulating data as models and value objects
4.1 Creating custom classes
4.2 Using the AppModelLocator
4.3 Binding view controls to data in the AppModelLocator
5. Making things happen
5.1 Creating event handlers in ActionScript within views
5.2 Creating custom events to call actions and to carry data
5.3 Creating command classes to process events and to update data and views
5.4 Mapping events to classes in AppController
6. Connecting with external data services
6.1 Loading xml and other data using HTTPService
6.2 Coping with security sand box restrictions
6.3 Creating and using an asynchronous service delegate
6.4 Accessing and using the results of a service delegate
7. Publishing your Flex application using SWFObject
Interested?
Cairngorm Flex Quickstart
Follow-up to My first small Cairngorm Flex application (with explanation) from Transversality - Robert O'Toole
Where necessary, I have included links to template files that can be added to a project. I have also included example code snippets that can be copied in to perform the common Cairngorm tasks.
Start page for this tutorial.
August 23, 2007
My first small Cairngorm Flex application (with explanation)
Follow-up to WiMIC Browser – my first big Flex application from Transversality - Robert O'Toole
Explanation
Here is a screenshot of the Navigator window for the project:
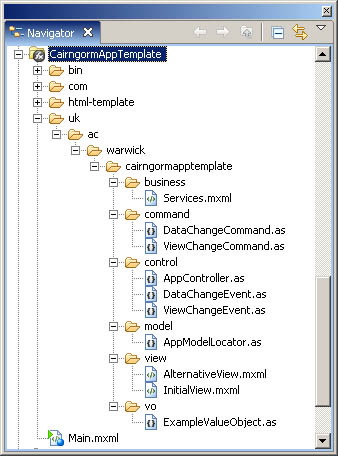
The Cairngorm source code is included in the "com" folder (although it could be compiled and included as an external library). The "uk.ac.cairngormtemplate" folder contains my application. This has six subfolders, each containing classes responsible for different parts of the MVC architecture: view, control, command, business (actually meaning data and comms services), model, vo (value object). As with all Flex applications, there is a single container mxml file, called Main.mxml (an mxml file is equivalent to a html file, with code, styles and visual components). I'll start my explanation of this app and Cairngorm with this top-level container.
The Main.mxml file contains four key items:
- a Services component - this contains all of the services used for connecting to external data sources etc;
- the AppController - this maps events onto commands, so that when a ui dispatches an event (a request for something to happen), the correct code does the required job;
- the AppModelLocator - this stores and indexes all of the data models used in the application, all of the data is stored in one place!
- a ViewStack listing all of the alternative user interface views that the app can display.
Here's the code for the ViewStack:
<mx:ViewStack width="100%" paddingBottom="10" paddingTop="10" resizeToContent="true" selectedIndex="{model.currentView}">
<view:InitialView />
<view:AlternativeView />
</mx:ViewStack>
There are two views in this application, an initial view and an alternative. Each view is defined in its own mxml file in the "uk.ac.cairngormtemplate.view" folder. Notice how the selectedIndex property of the ViewStack is bound to the .currentView property contained in the modelLocator (initially set at 0, which means that the first view in the stack is displayed). This means that the currently selected view may be changed by changing the model.currentView property (more on that below).
So now let's drill down into the InitialView component. We can then see the details of what is presented to the user, and what happens when the user responds to that interface.
InitialView is itself an mxml component based upon the standard VBox component. It contains some script and some UI components. Firstly, the script contains a bindable reference to the AppModelLocator singleton. This means that we can bind UI components to data in the AppModelLocator. There is in fact a text component that is bound to a value object (a class that wraps a set of value properties):
<mx:Text text="{model.messageVO.message}" />
Initially this displays the message "Hello everyone".
Below this text component there is a button "translate". Clicking this button calls an actionscript method in the script on the page. The method is called translate(). It could at that point do some validation, or request further input. However, in this case all that we want it to do is fire of a request for the text "Hello everyone" to be translated.
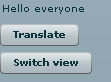
The least impressive Flex app ever
This is where Cairngorm starts:
private function translate():void
{
var cgEvent : DataChangeEvent = new DataChangeEvent("Dumelang");
CairngormEventDispatcher.getInstance().dispatchEvent( cgEvent );
}
The method creates an instance of the DataChangeEvent, passing it the new message "Dumelang". The DataChangeEvent is defined in the "uk.ac.cairngormtemplate.control" folder. It is a cairngorm event extended to carry our message. We can create events that can carry whatever data we need to be passed to a command. (For example, a user types their username and password into a login box, this is then wrapped in a LoginEvent, and the event dispatched. A LoginCommand receieves the event and attempts a login using a LoginDelegate and login service. If succesful, the command changes the current view to one appropriate to a signed in user).
The next step is to dispatch that event and its message to the Cairngorm controller. This should then get passed on to the required "command" object (the command object contains the code for executing the requested command). But how does the controller know which command object to use? Events are mapped on to commands in the control.AppController class:
public class AppController extends FrontController
{
public static const DATACHANGE_EVENT : String = "DATACHANGE_EVENT";
public function AppController()
{
addCommand( AppController.DATACHANGE_EVENT, DataChangeCommand );
}
}
Our request (to translate "Hello everyone") is then passed to a DataChangeCommand object. This is where we do the work that results in the translation. In this simple example, the .messageVO.message of the modelLocator is simply changed to read "Dumelang". However, we could instead refer to an English-Steswana dictionary to retrieve the translation. This might even require the use of an external data service. The DataChangeCommand would then delegate the work of sending this external request to a Delegate class in the "business" folder. The delegate, on retrieving the required translation, calls back to the DataChangeCommand to complete the requried command, or alternatively calls a seperate command.
So, with the text control on the current view bound to the .messageVO.message property in the modelLocator, and that property now altered (by DataChangeCommand) to "Dumelang" that is precisely what the end user sees on their screen.
But what if we also need to change the current view, for example to the AlternativeView control in the ViewStack? Easy. The command simply alters the .currentView property of the modelLocator. As the selectedIndex property of the ViewStack is bound to .currentView, it immediately changes.
In this example, at the end of DataChangeCommand, a second command is requested using a class that I have called ViewChangeEvent.
var cgEvent2 : ViewChangeEvent = new ViewChangeEvent();
CairngormEventDispatcher.getInstance().dispatchEvent( cgEvent2 );
This class calls ViewChangeCommand, which simply alternates between the InitialView and the DefaultView.
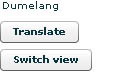
Look - it speaks Setswana! and now the view has changed to one with a white background! Hoorah!
Conclusion
This may be a simple example, but I can already see how using the Cairngorm framework will simplify the task of building very complex applications, resulting in better, more rational and sustainable code.
 Robert O'Toole
Robert O'Toole

 Please wait - comments are loading
Please wait - comments are loading
